The various equine respiratory pathologies can have a significant impact on the animal’s general health and compromise its ability to make any effort. In horses, they can result from a variety of factors, such as the environment, the level of health or the circulation of viruses and diseases.
How is the respiratory system affected by these diseases? How can they be prevented and recognised?
How the respiratory system works
The respiratory system is the part of the anatomy that enables horses to breathe and supply their muscles with oxygen. It is made up of a number of elements that subsequently condition the activity of all the other organs, such as the cardiovascular and muscular systems.
The respiratory system is made up of 6 components:
-
- Nostrils
- Pharynx
- Trachea
- Larynx
- Bronchial tube
- Lungs
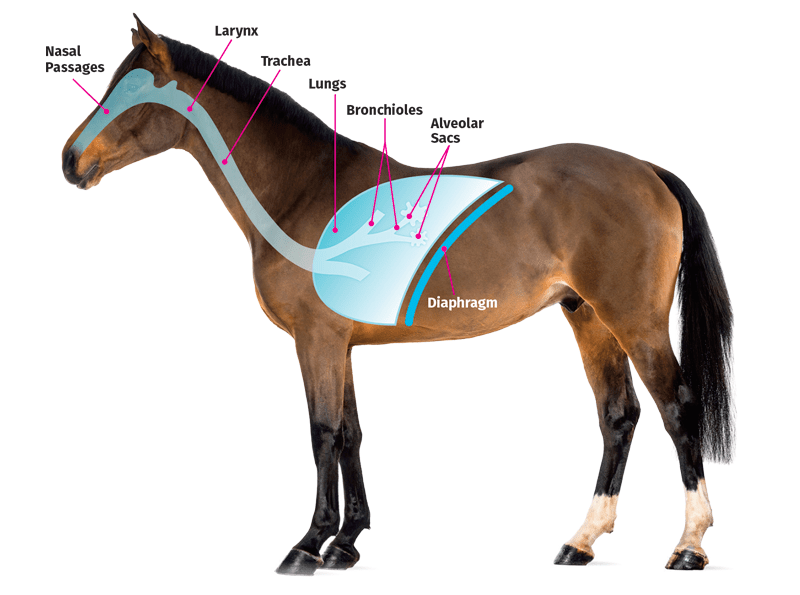
Schematic of the equine respiratory system by Anthony Deyo
Each has a different and distinct role in the processing of inspired air. The nostrils are the first point of contact for the air, which then passes into the larynx, pharynx and through the trachea. The next stage involves the bronchial tubes, giving rise to the bronchioles that divide the air into two for each lung.
The causes and risk factors for respiratory diseases
Respiratory illnesses in horses are common and can be caused by a number of different factors. Some are seasonal, others are linked to environmental or genetic factors, while still others are caused by infections.
Environmental management
Good environmental management is crucial to maintaining healthy respiratory tracts in horses. There are a number of essential points to consider, such as the quality of air in the stables, the quality of straw and hay, and exercise management. Stables need to be correctly ventilated and kept clean to avoid, for example, a pile of dust that is harmful to horses’ breathing. This can also be contained in straw and hay, if they are of poor quality. Taking your horse out of his box regularly allows him to breathe fresh air and reduces exposure to allergens in the stables.
If you’d like to find out more about the impact of stable air quality on a horse’s performance, read this article.
The genetic factor
Some horses may be genetically susceptible to developing respiratory problems. Some specific breeds may be more sensitive to certain conditions, or some horses may be hereditarily affected. Taking into account a horse’s genetic predisposition can help to prevent and anticipate a number of respiratory diseases.
Infectiours diseases
Infectious diseases represent a significant threat to the respiratory health of horses. Equine influenza and rhinopneumonitis, for example, are highly contagious infections that can lead to serious respiratory complications. Preventive measures, such as vaccination and isolation of sick horses, are essential to avoid the spread of these infectious diseases. It is important to know that 65% of horses are infected with HPE (rhinopneumonitis virus), but this remains inactive without reactivation.
The various equine respiratory problems
Respiratory diseases
Respiratory diseases are among the most common problems in equines and can have a variety of causes. Two of the most common respiratory conditions in horses are strangles and emphysema.
Strangles is a bacterial infection that affects the upper respiratory tract. It is caused by a bacteria that causes symptoms such as fever, cough, swollen glands under the jaw and a runny nose.
Emphysema is a chronic respiratory condition characterised by obstruction of the airways and distension of the pulmonary alveoli. Horses with emphysema usually have difficulty breathing, a persistent cough and may wheeze. This disease is often compared to asthma in humans.
Inflammatory diseases
Equine pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung tissue caused by infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses or fungi. It is a serious disease that can be life-threatening if not treated quickly and appropriately.
Pneumonia can be bacterial (caused by infection with bacteria) or viral (caused by infection with a virus). It is when their immune system is low that horses can contract bacteria. Their system can be affected by age, but in some cases by stress, transport or illness. Horses with bacterial pneumonia may present with fever, cough, runny nose and difficulty breathing.
Some viral infections, such as equine influenza virus or equine rhinopneumonitis virus, can also cause pneumonia in horses. Viral pneumonia can be particularly severe and lead to serious complications.
Viral diseases
Let’s go into more detail about these viral infections. Viral diseases are a frequent source of respiratory problems in horses. In addition to pneumonia, there is also equine rhinopneumonitis. This is caused by equine herpesvirus type 1 (EHV-1) and type 4 (EHV-4). In addition to respiratory symptoms, this viral disease can cause abortions in pregnant mares and lead to neurological complications. Highly contagious, every year we experience episodes of rhinopneumonitis requiring strict measures to be taken. This year, in February, the Oliva CSI experienced a case of rhinopneumonia and took the following measures: end of competition, incubation of horses from the same stable for 7 days, temperature check and regular tests.
Pulmonary haemorrhage
Pulmonary haemorrhage is a pathology that can be common in racehorses and eventing horses that are subjected to intense effort. It is characterised by an outflow of blood from the nostrils, which can be repeated and lead to breathing difficulties, coughing and reduced performance.
If you’d like to find out more about pulmonary hemorrhage and arrhythmia, we recommend this podcast.
Conclusion
Respiratory diseases can be varied and present major challenges for the health and well-being of horses. It is essential to take preventive measures, work with veterinarians to establish diagnoses and find appropriate treatments quickly.
SOURCES :
Anon, (2019). LES PRINCIPALES PATHOLOGIES RESPIRATOIRES CHEZ LE CHEVAL | Cheval Partenaire. [online] Available at: https://cheval-partenaire.fr/les-principales-pathologies-respiratoires-chez-le-cheval/ [Accessed 23 Jun. 2023].
audevard.com. (n.d.). L’appareil respiratoire du cheval. [online] Available at: https://audevard.com/espace-sante-cheval?slug=lappareil-respiratoire-du-cheval [Accessed 23 Jun. 2023].
Cgp-horsefeed.com. (2020). Emphysème et pathologies respiratoires. [online] Available at: https://www.cgp-horsefeed.com/blog/post/pathologies-respiratoires-chez-le-cheval-emphys%C3%A8me [Accessed 23 Jun. 2023].
Keywords: respiratory diseases, inflammatory, lungs, EnvA, CIRALE
Photo credit @Sarah Farnsworth